BG_RTK
About this model
This is a bond-graph model of the metabolism of generic receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) in the mammalian cell.
- INPUTS:
- Ligand (L) stimulus
- OUTPUTS:
- Change in molar amount of phosphorylated RTK K2Pn
- REACTIONS:
- Re1: the binding of L to one RTK (K1)
- Re2: formation of temporary complex of two RTK molecules which have dimerized, with ligand present (LK1 K2).
- Re3: autophosphorylation of second RTK in the dimer and simultaneous dissociation of dimer.
Model status
The current CellML implementation runs in OpenCOR.
Model overview
The following model of RTK action is based on what is widely known in literature.
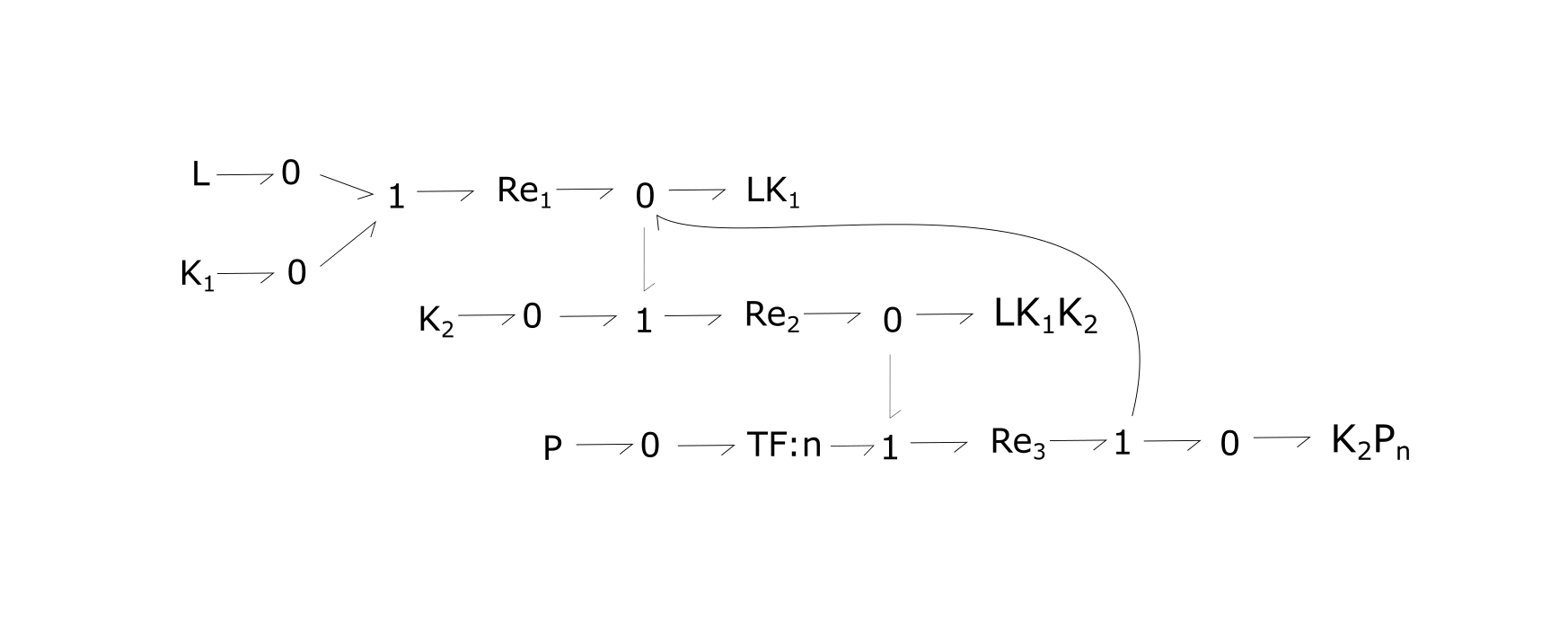
Fig. 1. Bond-graph formulation of the generic RTK network. Because this model is generic, n would change depending on the chosen reaction.
For the above bond-graphs, a '0' node refers to a junction where all chemical potentials are the same. A '1' node refers to all fluxes being the same going in and out of the junction.
| Abbreviation | Name |
|---|---|
| K | Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) |
| L | Ligand |
| Pi | Phosphate |
Parameter finding
A description of the process to find bond-graph parameters is shown in the folder parameter_finder, which relies on the:
- stoichiometry of system
- kinetic constants for forward/reverse reactions
- If not already, all reactions are made reversible by assigning a small value to the reverse direction.
Here, this solve process is performed in Python.

