Kidney knowledge
Kidney
The kidney works by filtering out unwanted solutes from blood in order to make urine, and reabsorbs what is needed in order to maintain homeostasis. A kidney is made up of nephrons receiving blood via the renal artery, and returns the filtered blood to the renal veins. Water is also reabsorbed through aquaporins along every stage of the nephron, to varying degrees. The filtered-out urine flows towards the bladder through the ureters.
Pictures
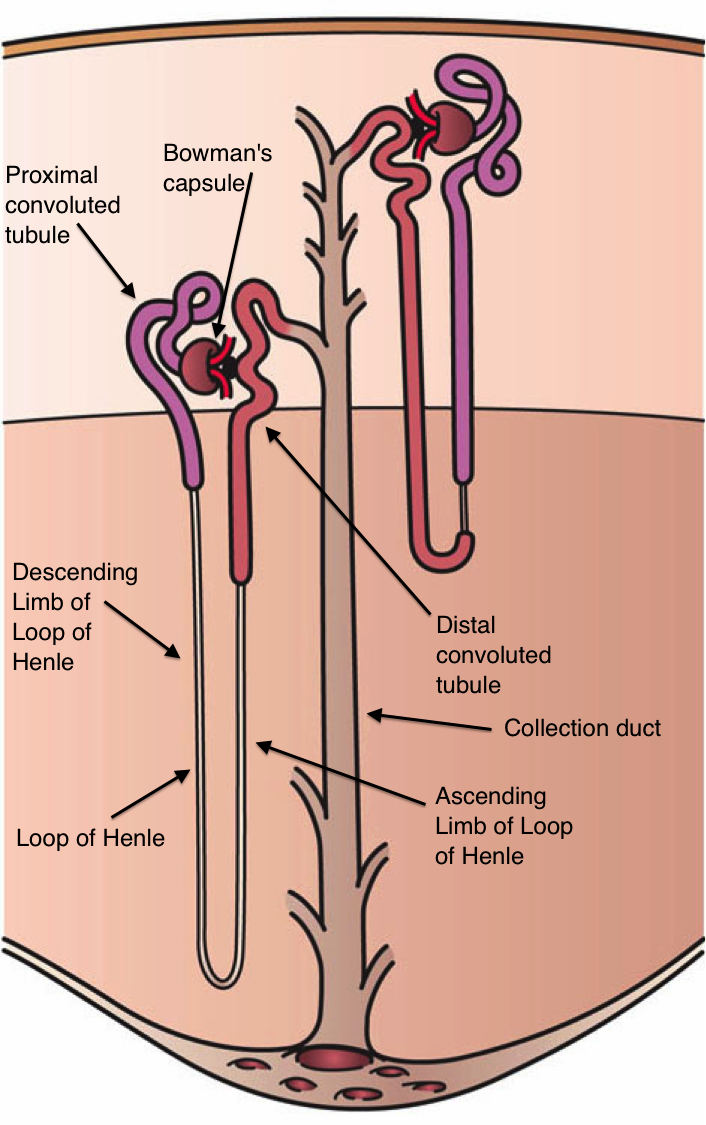
Fig. 1. The nephron
| Abbreviation | Name |
|---|---|
| CD | Collecting Duct |
| CNT | Connecting Tubule |
| DCT | Distal Convoluted Tubule |
| IMCD | Inner Medullary Collecting Duct |
| JGA | Juxtaglomerular Apparatus |
| OMCD | Outer Medullary Collecting Duct |
| PCT | Proximal Convoluted Tubule |
| TAL | Thick Ascending Limb |
| tDL | thin Descending Limb |
Solute transport
The following list contains the known membrane transporters along the nephron.
| Abbrev | Channel name | Location | Membrane | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE1 | Anion exchanger 1 | PCT/OMCD | A (PCT)/B (OMCD) | Cl- in/HCO3- out |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | DCT/CCD/IMCD | B | Cl- out |
| CLC-K | Kidney chloride channel | TAL/DCT/CD | B | Cl- out |
| Cldn 2/12/16/19 | Claudin | PCT (Cldn 2/12)/TAL (Cldn 16/19) | P | Ca2+ out |
| ENaC | Epithelial sodium channel | CNT/CD | A | Na+ in |
| Glut1 | Glucose transporter 1 | late PCT | B | glucose in |
| Glut2 | Glucose transporter 2 | early PCT | B | glucose in |
| H-ATPase | Hydrogen ATPase | PCT/CNT/CD | A | H+ out |
| H-K-ATPase | Hydrogen/potassium ATPase | CNT/IMCD/OMCD | A | H+ out/K+ in |
| KCC | K/Cl cotransporter | PCT/TAL/IMCD | B | Cl- out/K+ out |
| Na-Pi2 | Sodium/phosphate cotransporter 2 | PCT | A | Na+ in/PO42+ in |
| NCC | Sodium chloride cotransporter | DCT/CNT | A | Na+ in/Cl- in |
| NCX1 | Sodium/calcium exchanger | CNT/DCT | B | Na+ in/Ca2+ out |
| NHE3 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger | PCT/TAL/DST | A | Na+ in/H+ out |
| NHE4 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger | PCT/TAL | A | Na+ (or NH4+) in/H+ out |
| NKA | Sodium/potassium ATPase | throughout | B | 3Na+ out/2K+ (or NH4+) in |
| NKCC2 | Sodium/potassium/chloride cotransporter | TAL | A | Na+ in/2Cl- in-/K+ (or NH4+) in |
| PMCA | plasma membrane calcium ATPase | PCT/DCT/CNT | B | Ca2+ out |
| ROMK | Renal outer medullary potassium channel | TAL/CNT | A | K+ out |
| SGLT1 | Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 | late PCT | A | Na+ in/glucose in |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 | early PCT | A | Na+ in/glucose in |
Solutes: Sodium Na+, chloride Cl-, potassium K+, hydrogen H+, bicarbonate HCO3-, ammonum NH4+, phosphate PO42+ Membrane: A apical (to filtrate), B basolateral (to blood), P paracellular (to interstitial space). Direction: movement of solute under normal physiological conditions.
Water transport
The following list contains the known aquaporin (AQP) isoforms along the nephron, which transport water across the cell membrane.
| Location | AQP | Membrane | Direction | Reab |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT | 1 | A | in | |
| 1 | B | out | 70 | |
| PCT | 7 | A | in | |
| tDL | 1 | A | in | |
| 1 | B | out | 20 | |
| CD | 2 | A | in | |
| 3 | B | out | ||
| 4 | B | out | 0-9 |
'Reab' refers to the total water reabsorption amount of the section. 'Direction' is the movement of water relative to the cell the AQP is present in.
Literature
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| A mathematical model of the inner medullary collecting duct of the rat: acid/base transport | Weinstein |
| Coupling of renal sodium and calcium transport: A modeling analysis | Hakimi et al. |
| Renal water transport in health and disease | Feraille et al |
Existing models
| Title |
|---|
| Na+/H+ Exchanger (NHE3) Model |
| Cl-/HCO3- Exchanger (AE1) Model |
| H+/K+ ATPase (Weinstein, 1998) |

